Global warming and climate change are terms we use to describe the rise in the average temperature of the earth. As our planet warms, we observe temperature changes on the earth’s surface, in our oceans, and within the atmosphere.
Throughout history, the earth’s global climate has gone through numerous cycles of both warming and cooling. In the last 600,000 to 700,000 years alone, scientists believe the earth has seen seven cycles of glacial advancement and retreat. This is a clear indicator of historic periods of global warming and cooling.
There is something different about the current warming cycle, however. Most scientists agree this is a result of human influence on the ‘greenhouse effect’. This phenomenon relates to the abundance of greenhouse gases within our atmosphere.
What Are Greenhouse Gases?
Greenhouse gases (or GHG’s) are gases contained within our atmosphere that have the potential to absorb infrared radiation. These gases absorb heat reflected from the earth that would otherwise be lost to space. They are vital for helping to keep our planet warm and inhabitable.
The primary greenhouse gases we can find within the earth’s atmosphere are shown in the following table.
| Greenhouse Gas | Chemical Formula | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Vapor | H2O | Evaporated water (predominantly from the sea.) |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | Industry and fossil fuel combustion in general, becoming more concentrated due to deforestation. |
| Methane | CH4 | Industry and fossil fuel combustion, livestock, landfill/waste, agriculture, and biomass/biofuels. |
| Nitrous Oxide | N2O | Industry and fossil fuel combustion, agriculture, chemical engineering. |
| Ozone | O3 | Created when Ultraviolet Radiation (UV) from the sun makes contact with the oxygen in the atmosphere. Also, thunderstorms (lightning) and artificial ozone manufacturing. |
Greenhouse Effect
We use the term ‘greenhouse effect’ to describe the natural process whereby greenhouse gases trap thermal energy within the earth’s atmosphere. Without the greenhouse effect, the earth would be a very cold and inhabitable place.
Greenhouse gases allow sunlight to pass through the atmosphere. The surface of the earth (including its oceans) will partially absorb some of this solar radiation. The remaining solar energy will bounce away from the earth in the form of infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases will then absorb some of this radiation, helping to keep our planet warm.
Although the greenhouse effect is a natural process vital to sustaining life on earth, it has become too effective in recent times. Scientists believe this is due to an abundance of greenhouse gases within the atmosphere. This abundance of greenhouse gases is helping to warm our planet at a faster rate than we have ever seen before.
How Much is The Earth Warming?
The earth has been warming most years since a brief cooling period of around ten years in the early 1900s. This is according to data provided by NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS). The same data also suggest we have been experiencing rapid warming of the earth since the mid to late 1970s.
The following chart illustrates the change in global surface temperature since 1880, relative to 1951 to 1980 average temperatures. The data has been sourced from NASA/GISS.
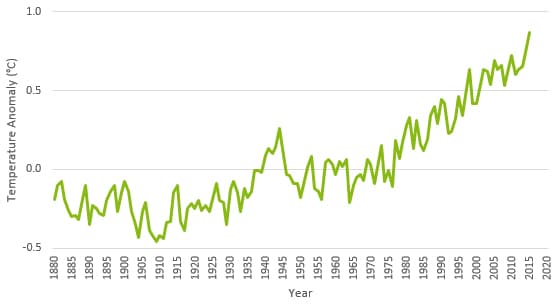
Chart illustrating the change in global surface temperature of the Earth since 1880.
The Effects of Climate Change
Scientists project that global warming will have numerous effects on the earth and its oceans. We can already observe some of these effects today:
- Glacial retreat as a result of global temperature rise.
- Lower volumes of Arctic sea ice and other ice sheets.
- Rising sea levels as a result of ice melt. Sea level rise is already starting to affect some human settlements.
- More frequent and extreme weather events (such as drought and heat waves.)
- Disruption to plants and animals.
With scientists in agreement that global warming is set to continue for many years ahead, the effects of global warming are likely to get worse and be felt further afield.
Can Global Warming Be Stopped?
The short answer to this is no. Global warming is a natural cycle that’s important in helping to sustain life on earth. However, what we can stop (or at least reduce) is the impact that humans have on the greenhouse effect. This will help our planet to follow a more natural warming/cooling cycle, rather than a man-made cycle.
Governments across the world are committed to reducing climate change. It does, however, remain to be seen whether or not this positive attitude will have any long term impact.